Cloud computing has made significant progress, but not many companies have successfully migrated to it. The key to a successful migration is a well-planned, step-by-step process that simplifies and speeds up the process. We have assisted numerous clients in adopting a transformation roadmap for their cloud migration journey, and we will be sharing step by step approach in this blog. But before that, let’s check some facts and figures that demonstrate where the trend is moving ahead in and around cloud adoption and migration.
- According to Precedence Research, the cloud computing market is projected to exceed $1 trillion globally by 2028.
- VMware states that modernizing and integrating applications with public cloud services is a crucial priority in the upcoming three years.
- Accenture suggests that migrating your business to the public cloud can result in up to a 40% reduction in Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
- Virtana reports that 80% of organizations are utilizing multiple public or private clouds.
- Osterman Research states that the world produces 2.5 quintillion bytes of data every day.
- The State Of Cloud Cost Intelligence 2022 Report by CloudZero reveals that only 3 out of 10 organizations have a clear understanding of their cloud costs.
These statistics reveal that the cloud computing market is rapidly expanding, and businesses are increasingly adopting cloud services to modernize their applications, reduce costs, and manage data. However, the lack of cloud capabilities in cloud deployment and management indicates a need for better cloud consulting, cloud development, and cloud management to optimize spending.
What Does A Cloud Migration Service Look Like?
A cloud migration service is a professional service that helps businesses move their data and applications from their on-premises infrastructure to a cloud-based environment. The service typically includes a thorough assessment of the business’s current infrastructure, identification of which data and applications are suitable for migration, planning and implementation of the migration process, and ongoing support to ensure the smooth functioning of the cloud environment. A cloud migration service sometimes also includes training to help the business’s staff get up to speed on the new cloud-based environment. The ultimate goal of a cloud migration service is to help businesses achieve the benefits of cloud computing, such as improved scalability, cost savings, and flexibility.
Let’s explore step by step processes of cloud migration service planning and implementation:
Planning
The most crucial aspect of a cloud migration initiative is planning. This stage centers on program management arrangement, analysis of the portfolio, and designing the cloud architecture and operating model.
- Program management setup: During the planning phase, the program management team is responsible for overseeing various aspects, such as strategy development, program governance, and benefits realization. The program management team’s duties include ensuring strong leadership, implementing change management, aligning program strategy, maintaining strict project execution standards, and enforcing decision-making governance.
- Portfolio analysis: The analysis of the application portfolio is essential for a cloud migration program as it provides an accurate representation of the applications that are in scope. This analysis includes information on application dependencies, which helps in planning the sequence of application migration and strengthens the business case for cloud migration.
- Cloud foundation and operating model layout: A critical component of the cloud migration program is the establishment of a cloud foundation and operating model layout. The Cloud foundation includes Landing Zones, which are standardized sets of secured cloud infrastructure with built-in policies, standards, guidelines, and centrally managed services. Establishing a robust foundation through Landing Zones is crucial for creating a scalable and sustainable enterprise AWS cloud model. As cloud computing becomes the paradigm for delivering business, technology operating models must evolve to add more cloud-centric capabilities. The cloud operating model provides a framework for combining the core elements in a more agile, productive, and valuable way.
Assessment
In the assess phase of a cloud migration program, applications are analyzed in detail to determine their future disposition. The cloud architecture and operating model provide a solid foundation for migrations.
- Macro-analysis: Macro-analysis is conducted to analyze the applications using a cloud readiness and assessment framework based on business value, IT efficiency, and cloud suitability. This analysis ensures a clear migration roadmap and identifies enterprise-wide concerns related to security, networking, technical, operational, organizational, regulatory, and financial aspects.
- Microanalysis: Once the macro-analysis is complete, the program moves on to microanalysis, which involves a deeper understanding of the current state architecture and the definition of cloud architecture based on patterns identified during macro-analysis. The microanalysis concludes with the preparation of a detailed migration plan and effort estimates.
- Cloud foundation and operating model design: The design of the cloud foundation and operating model should adhere to enterprise security and networking policies. The account and VPC structure needs to be designed based on cost allocation, resource management and ownership, and security and compliance isolation. The core elements of the cloud operating model are people, process, and technology, which should evolve to achieve the cloud operating model goals, thereby increasing business and operations value. People skills and experience are geared towards becoming more cross-functional, processes are realigned around services, and tools and technologies are selected for the effective implementation and automation of processes.
Setting Up Cloud Landing Zone
Building a landing zone in cloud migration service involves setting up a pre-configured environment that provides a foundation for secure, well-architected, and scalable cloud environments. It typically includes core infrastructure components such as identity and access management, network architecture, security controls, and monitoring tools.
The purpose of a cloud landing zone is to provide a standardized set of best practices for cloud infrastructure management, which can be reused across multiple projects to accelerate cloud adoption, improve security, reduce costs, and enhance agility. By establishing a landing zone, organizations can ensure a consistent approach to cloud infrastructure management and provide a secure and scalable foundation for the migration of workloads and applications to the cloud. This includes defining governance policies, establishing network connectivity, configuring security controls, and setting up monitoring and logging capabilities. Let’s understand them in more detail:
- Defining Governance Policies: Governance policies define rules and guidelines for managing cloud resources, and help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This includes policies for resource provisioning, access management, data management, and budget management. For example, governance policies might dictate that only approved users can provision new resources, or that data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Establishing Network Connectivity: Network connectivity is critical for cloud environments, as it provides access to services and resources, as well as connectivity between different components. Establishing network connectivity involves configuring network infrastructure components such as virtual private networks (VPNs), subnets, and routing tables. This ensures that resources can communicate with each other and with on-premises resources securely.
- Configuring Security Controls: Configuring security controls involves implementing a range of measures to protect cloud environments from threats and vulnerabilities. This includes identity and access management, encryption, network security, and compliance monitoring. For example, security controls might dictate that all user access requires multi-factor authentication, or that all data must be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
- Setting Up Monitoring and Logging Capabilities: Monitoring and logging capabilities are critical for identifying and responding to security incidents and performance issues. This involves configuring tools to monitor resource utilization, network traffic, and system logs, as well as setting up alerts for events that require attention. This enables administrators to proactively identify issues and address them before they become major problems.
See Also: In the case of AWS, since the introduction of Control Tower companies are migrating from the landing zone to AWS Control Tower. AWS Control Tower enables setting up a well-architected and managed environment for AWS platform.
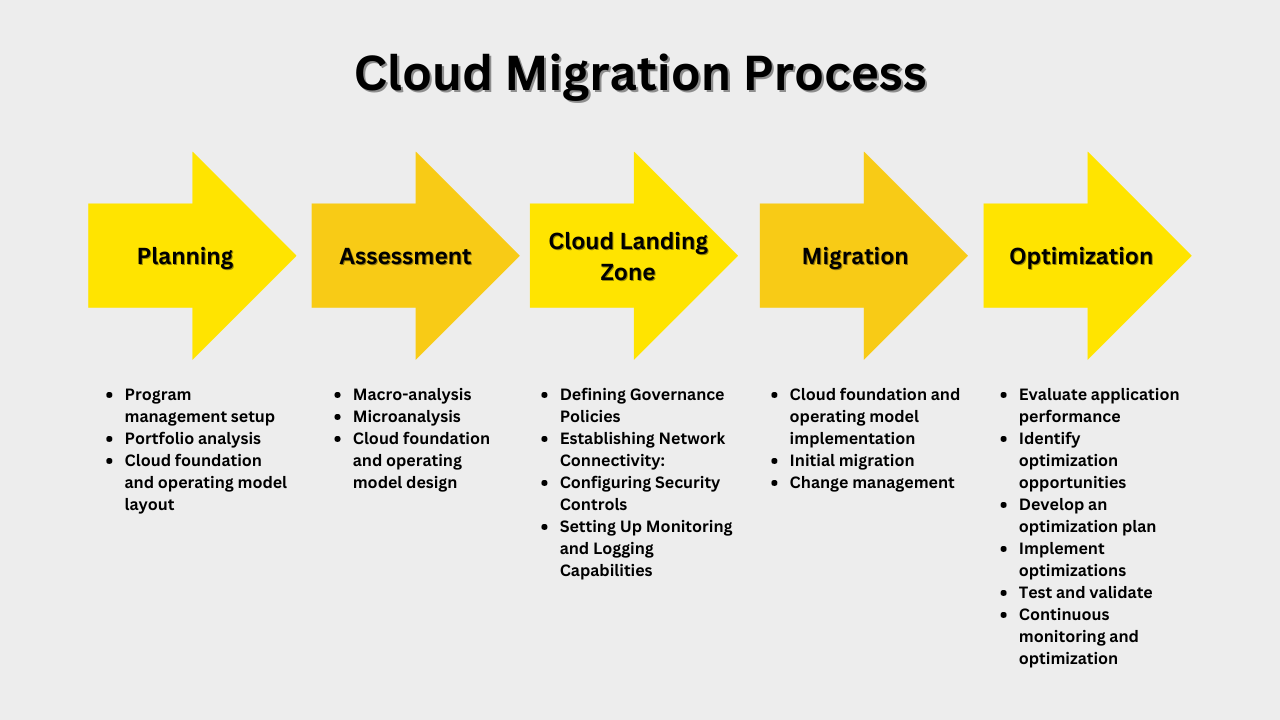
Migration
During the implementation phase of a cloud migration program, the foundation cloud architecture and operating model are put into effect, and a set of applications identified as “quick wins” are migrated. It’s crucial to take a proactive approach to change management during this phase.
- Cloud foundation and operating model implementation: The Cloud foundation and operating model implementation involves the setup of Landing Zones, including accounts, VPC, network connectivity, IAM Roles, policies, and deployed workflows as discussed above. Shared services and tools are provisioned, and key processes are rolled out in the cloud operating model, with teams mapped to new cloud-centric roles. Subsequent processes are then rolled out, leveraging key learnings from existing implementations to ensure seamless integration with current systems through the installation of selected tools.
- Initial migration: The initial migration involves the migration of a set of applications as quick wins, with varying complexities across different business units. This successful migration helps to understand the portfolio and builds confidence in the applications team, establishing a foundation for repeatable migration patterns.
- Change management: Effective change management is pivotal to the success of a cloud migration program. Change champions are involved to ensure co-creation of future roadmaps and smooth cultural shifts, with continuous knowledge sharing and training to evolve skills and include them in the transformation journey.
Read Also: What Are Cloud Migration Challenges To Consider?
Optimization
Migrating an application to the cloud can provide an enterprise with numerous benefits, such as scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, migration alone is not enough to fully realize these benefits. Optimization is an essential part of the cloud migration process, and without it, an enterprise may not be able to achieve the full value of the cloud.
Optimization after cloud migration involves identifying areas where the application can be improved to run more efficiently, reduce costs, and improve performance. This can include optimizing infrastructure, improving application architecture, and making code modifications. Without optimization, an application may continue to experience performance issues or high costs, negating the benefits of cloud migration. Designing and implementing optimization services after cloud migration.
- Evaluate application performance: To evaluate application performance after cloud migration, you will need to measure performance metrics such as response times, throughput, and resource utilization. You can use a variety of monitoring and analytics tools to gather this data, such as cloud-based monitoring and logging services, or open source tools like Prometheus and Grafana.
- Identify optimization opportunities: Based on the performance data you have gathered, you can identify specific areas of the application that could benefit from optimization. This could include areas such as database access, network latency, or infrastructure configurations. It’s important to focus on areas that are impacting the user experience or that are driving up costs.
- Develop an optimization plan: Once you have identified the optimization opportunities, you can create a plan that outlines the specific optimizations that will be implemented, as well as the timeline and resource requirements for each optimization. It’s important to prioritize the most impactful optimizations and ensure that you have the necessary resources and expertise to execute on the plan.
- Implement optimizations: Depending on the nature of the optimization, this step may involve modifying code, changing infrastructure configurations, or integrating new tools or services. For example, if you identified database access as a bottleneck, you might implement a caching layer to improve performance. During this phase, it’s important to carefully monitor the application to ensure that optimizations are not negatively impacting performance.
- Test and validate: Once optimizations have been implemented, it’s important to validate that the application is performing better than before. This may involve additional performance testing or monitoring, as well as user acceptance testing to ensure that the changes have not introduced any new issues or errors.
- Continuous monitoring and optimization: Optimization is an ongoing process, so it’s important to continue monitoring and optimizing the application over time. This may involve periodic reviews of performance metrics, identification of new optimization opportunities, and ongoing tweaks and refinements to the application and infrastructure.
Designing and implementing optimization services after cloud migration requires a deep understanding of the application and the cloud environment, as well as the ability to identify and execute on optimization opportunities. It also requires ongoing monitoring and optimization to ensure that the application continues to perform efficiently and effectively over time.
See Also: How Total Cost Of Ownership Is Calculated For Cloud Platform?
How Long Does Cloud Migration Take?
Migrating email and document management in a medium project usually takes 2-4 months, while more complex server setups and cloud-native service configuration can take 6-24 months. The timeline for application migration varies as it involves planning, training, and application modification based on the organization’s pace.
Some organizations may need to quickly migrate their data and applications to the cloud. For example, many companies accelerated their cloud migration approach in 2020/2021, to support remote work, online transactions, and data storage.
How Much Does Cloud Migration Cost?
Moving your organization’s infrastructure to the cloud offers various benefits, but it comes at a cost, especially when migrating at an enterprise level. The average total for cloud migration costs can range from $5,000 for smaller workloads all the way up to $500,000 and beyond for larger tasks.
In order to arrive at a more accurate estimate, it’s crucial to start considering the expenses of cloud migration early in the process of moving from on-premises hardware to third-party managed cloud solutions. Apart from the cost of the new cloud-based service, other expenses and savings should be analyzed for their impact on your business. Here’s a comprehensive overview of the financial impacts you need to consider when preparing to move to the cloud.
Calculating the cost of cloud migration involves identifying and estimating the various costs associated with the migration process. Here are the steps to calculate cloud migration cost:
- Identify the Scope: The first step is to identify the scope of the cloud migration, which includes the applications, data, and infrastructure to be moved to the cloud.
- Identify the Cloud Service Provider (CSP): Choose a cloud service provider that meets your organization’s requirements, budget, and long-term goals.
- Estimate Cloud Infrastructure Costs: Estimate the cost of cloud infrastructure, which includes computing resources (virtual machines, containers, storage), network resources (bandwidth, traffic), and cloud services (databases, load balancers, backups).
- Estimate Migration Costs: Estimate the cost of migration, which includes planning and preparation, data transfer, application modification, testing, and training.
- Identify Licensing and Subscription Costs: Identify any licensing or subscription costs for cloud services or applications that the organization will use in the cloud.
- Calculate Post-Migration Costs: Calculate the ongoing costs, such as cloud service fees, maintenance, and support costs.
- Compare the Costs: Compare the total cost of cloud migration with the organization’s existing infrastructure costs, including hardware, software, and maintenance costs.
- Consider the ROI: Consider the potential return on investment (ROI) of cloud migration, such as increased agility, scalability, and cost savings.
See Also: What are the benefits of cloud migration?
How Does Cloud Migration Impact Your Business?
Cloud migration can impact a business both from the inside and the outside. Let’s understand them.
- Impact on internal operations: When a business migrates to the cloud, it can have a significant impact on its internal operations. This is because the cloud offers new capabilities and opportunities that can change how the business operates. For example, the cloud can enable a more agile, flexible, and scalable IT infrastructure that allows for faster and more efficient application development and deployment. This, in turn, can lead to increased productivity, faster time-to-market, and reduced costs.
- Impact the workforce: Cloud migration can also impact the workforce, as it may require new skills, processes, and roles. For example, the business may need to invest in training and development to ensure that its employees are proficient in working with cloud-based technologies. It may also need to reorganize its IT teams to align with the new structure and responsibilities that come with cloud-based services.
- Impact how customers perceive and interact with the business: Externally, cloud migration can impact how customers perceive and interact with the business. For example, the cloud can enable new services and features that were previously not possible, leading to improved customer experiences and satisfaction. The cloud can also provide better data management capabilities, leading to improved data security, compliance, and privacy.
- Impact the business’s market positioning and competitive advantage: Cloud migration can impact the business’s market positioning and competitive advantage. For example, it may allow the business to enter new markets, offer new products or services, or improve the speed and quality of delivery. It can also improve the business’s ability to respond to changing market conditions and stay competitive.
Read Also: How FinOps Help In Cloud Cost Optimization?
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, cloud migration services provide businesses with the opportunity to harness the power of the cloud to improve their operations and achieve significant cost savings. Through careful planning, implementation, and ongoing support, a cloud migration service can help businesses smoothly transition from their on-premises infrastructure to a cloud-based environment. The benefits of cloud computing, such as improved scalability, increased efficiency, and better data security, make cloud migration a smart investment for businesses of all sizes. If you’re considering a move to the cloud, a cloud migration service can provide the expertise and guidance you need to ensure a successful migration and reap the benefits of cloud computing for years to come.




