Information of any kind has been crucial since ages and keeping them secret remains a tough job since then. In today’s digital world, when someone mentions ‘data protection’, they mean securing information be it people’s personal information or financial data or sensitive business information like intellectual properties, business strategies, employee information, customer information, legal information or operational information. Sensitive business information can vary depending on the industry and specific business.
But, with the widespread adoption of technology and cloud solutions in our daily lives, we are becoming more reliant on it. This means that we are also becoming more vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Cyber criminals are becoming more sophisticated in their attacks, using new and advanced techniques to breach security systems.
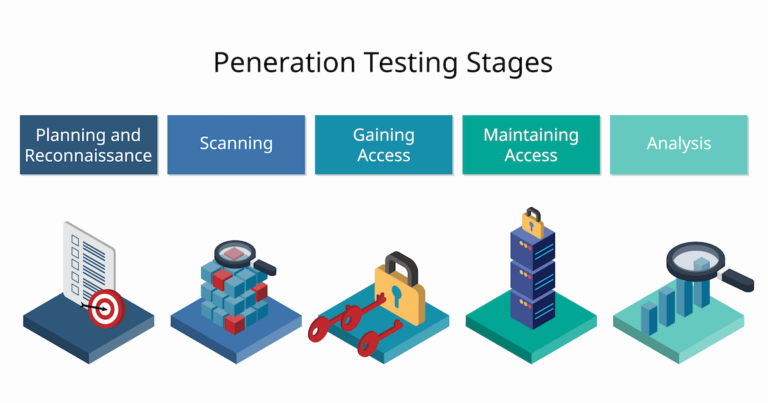
In those scenarios, it is important to adopt proactive approaches to ensure cloud security for smooth business operations. A business has two options when it comes to ensuring sound cybersecurity i.e. performing penetration tests. But there lies confusion that is to whether to perform internal or external penetration tests for enterprise applications and networks.
Internal penetration testing assesses the level of risk posed by a hypothetical hacker who has access to the internal network, simulating an attack from within the organization, such as by an employee. On the other hand, external penetration testing focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in internet-facing assets, such as email, web, and FTP servers. This type of test is typically conducted from the perspective of an external attacker with no prior knowledge of the organization.
What Are The Internal Threats To Business?
Human error accounts for more than 95 percent of security breaches and it begins from the careless actions or malicious intent of an insider. Since they are considered someone who is trusted, they may have privileged access to crucial business information like client’s details, financial data, etc. As an insider, a person can be a threat to a business in different ways, such as:
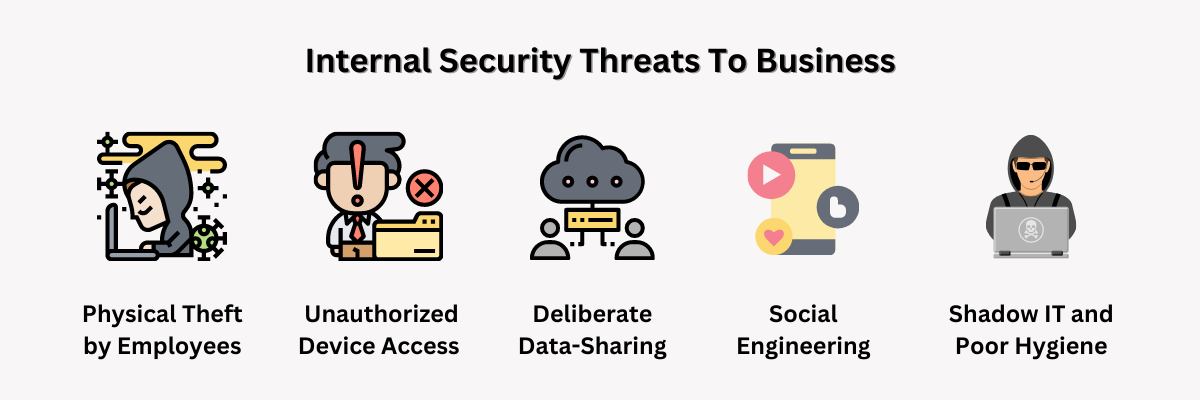
Physical Theft by Employees
Employees have the ability to physically operate various devices and equipment. On occasions, they may falsely report a device as lost when, in fact, they have stolen it. In some cases, when an employee departs the company, they may not return a device belonging to the organization, citing that nobody asked for it. Such occurrences of device theft render the company exposed to cybersecurity risks like data breaches, unauthorized access, and other forms of cybercrime.
Use of Unauthorized Devices
With the advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, a significant number of employees are currently working from home on their personal devices, a practice commonly referred to as Bring Your Own Device (BYOD). Such personal devices may have insufficient security measures in place, which increases the possibility of malware attacks and virus infections. Moreover, when utilized on unsecured WiFi networks, the confidential information stored on these devices could be intercepted by cybercriminals, particularly if the data is not encrypted with adequate safeguards.
Deliberate or Inadvertent Data-Sharing
When employees or other insiders share data either intentionally or unintentionally, it poses a significant internal risk to the company. Such acts may involve posting information about the organization on social media platforms, sending unencrypted emails to incorrect recipients, disclosing confidential company secrets in public places, or unknowingly allowing a threat actor to capture their keystrokes through a keylogger.
Social Engineering
Due to inherent human traits, such as trust in others and emotional responses like fear and panic, individuals may become vulnerable to manipulation by cybercriminals. These criminals may exploit such “weaknesses” to coerce employees into divulging their login credentials, sharing confidential information, installing malware, or even transferring funds.
Shadow IT and Poor Cybersecurity Hygiene
Shadow IT pertains to the use of unsanctioned software, applications, services, or devices that are neither authorized nor monitored by the IT department. This practice results in significant security loopholes, allowing any threat actor to exploit these applications or devices to gain access to the company’s network or data. Furthermore, substandard cybersecurity practices, such as using weak passwords and clicking on links embedded in emails from unfamiliar senders, pose a grave risk to cybersecurity.
What Are The External Threats To Business?
As per the Cyber Security Breaches Survey 2022 released by the UK government, 39% of the country’s businesses reported experiencing a cyber attack in the past year. Among these businesses, 31% stated that they were targeted at least once every week, while one in five reported experiencing an adverse impact as a consequence of the attack. Concerning material repercussions, the average estimated cost of cyber attacks for all businesses in the last 12 months was £4,200, although for medium and large enterprises, this figure increased significantly to £19,400.
A successful cyber attack has the potential to inflict significant harm on your business. It can impact your profitability, damage your reputation, and undermine customer trust. The consequences of a security breach can be broadly classified into three categories: financial, reputational, and legal.
Financial cost of cyber attack
Cyber attacks often result in substantial financial losses arising from several reasons such as theft of corporate information, theft of financial data such as bank details or payment card information, theft of funds, disruption to trading such as the inability to conduct transactions online, and loss of business or contracts. In addressing the breach, businesses will typically incur expenses related to repairing affected systems, networks, and devices.
Reputational Damage
Trust forms a crucial component of a customer’s relationship with a business. Cyber attacks have the potential to jeopardize a company’s reputation and diminish the trust placed by its customers. This, in turn, may result in loss of customers, decline in sales, reduction in profitability and other business losses. The repercussions of reputational damage may even extend to suppliers and impact relationships with partners, investors, and other third parties associated with the business.
Legal Consequences Of A Cyber Breach
Data protection and privacy regulations mandate that you ensure the security of all personal information in your possession, whether it pertains to your customers or your staff. If such data is intentionally or unintentionally compromised, and you have not implemented adequate security measures, you may be subject to penalties and regulatory action.
How Do Internal and External Threats Differ?
Both internal and external risks can pose significant dangers to any organization. However, they manifest in different ways and require distinct measures to mitigate them. But both the processes go through standard penetration testing phases to secure enterprise applications.
Internal hazards, such as accidental data leaks or phishing attacks, can be addressed through better cybersecurity training or stricter data segregation protocols to prevent insiders from accessing data they shouldn’t. Insiders are already within the organization’s boundaries, so security teams require different tools to deal with them.
On the other hand, external threats need to penetrate your network first. As a result, you need to employ tools like penetration testing, packet inspection, and multi-factor authentication to keep unwanted visitors out. Additionally, you need to closely monitor any irregular data flow outside of your organization since it may be a sign of an outsider taking valuable data.
In essence, insider and outsider threats exhibit distinct behaviors. Although each group may pose comparable risks, they are not identical, and therefore security teams will need tools appropriate for each type of threat.
List of Internal Vs External Penetration Tests
Internal and external penetration tests are performed differently to identify different attack types. Internal tests are focused on identifying bugs that could be exploited by malicious employees or business partners within the organization having privilege access. Whereas external tests looked over security vulnerabilities from outside the system. Here is a list of penetration tests ideally a security engineer performs when required to secure the application from possible security issues.
| Internal Penetration Test | External Penetration Test |
| Computers, workstations, and portable devices | Error control test |
| Points of entry | Configuration & Deployment Management Test |
| Servers | Authentication Test |
| HVAC systems with internet access | Identity Regulating Test |
| Wireless networks | Authorization Test |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Input validating test |
| Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) | Cryptography test for weakness |
| Firewalls | Intended business behavior Test |
| NA | Client Side Test |
Internal Vs. External Penetration Testing Methodologies
The methodologies used in pen testing can vary depending on the types of vulnerabilities that are being sought. For example, if the goal is to test for web application vulnerabilities, the tester may use a methodology that involves identifying common attack vectors such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, or input validation errors. On the other hand, if the goal is to test for network vulnerabilities, the tester may use a methodology that involves identifying open ports, weak passwords, or misconfigured devices.
Henceforth, the choice of methodology depends on the specific objectives of the pen test and the types of vulnerabilities that the tester is trying to identify. A good pen tester will tailor their methodology to the specific system or network being tested, taking into account factors such as the technology stack, the threat landscape, and the level of access that is being granted for the test. Let’s look at the list of penetration testing methodologies used in different cases of internal and external penetration testing needs.
| Internal Penetration Testing Methodologies | External Penetration Testing Methodologies |
| Internal Network Scan | IDS/IPS Testing |
| Port Scan and Fingerprinting | Scrutinizing for public information and information leakages. |
| Manual Vulnerability Testing and Verification | Manual testing identified vulnerabilities. |
| Firewall and ACL Testing | Footprinting |
| Password Strength Test | Password Strength Test |
| Network Security Controls Test | Data breach test |
| Database Security Controls Test | NA |
| Internal Network Scan, Trojan test | NA |
| Privileges Escalation Testing | NA |
How Internal And External Penetration Testing Minimize The Impact Of Cyber Attacks On Business?
Even the most resilient businesses can suffer devastating consequences from security breaches. Therefore, it is crucial to proactively manage the risks through internal and external penetration testing. By implementing effective cybersecurity practices regularly and proactively, businesses can:
- Minimize the impact of an attack
- Report the incident to the relevant authority
- Clean up the affected systems
- Resume business operations as quickly as possible.
What Does Internal Vs External Penetration Testing Service Look Like?
| Internal Penetration Testing Service | External Penetration Testing Service |
| An internal attacker is someone who has authorized access to an organization’s information system but uses it for malicious purposes. It is imperative to identify such vulnerabilities to prevent insider threats. To do this, an organization needs to maintain an in-house security team. This team is responsible for conducting regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. | An external attacker is someone who does not have authorized access to an organization’s information system but uses various means to gain unauthorized access to the system. It is essential to identify such vulnerabilities to prevent external threats. One way to identify vulnerabilities from an external attacker’s viewpoint is by outsourcing testing. |
| However, maintaining an in-house security team can be expensive due to the need to hire skilled professionals and purchase necessary equipment and software. | Outsourcing testing is cost-effective as it does not require an organization to maintain a team of security professionals. Instead, an external security firm is hired to conduct the testing. |
| Despite the cost, having an in-house security team provides a regular way of ensuring security. This team can monitor the organization’s systems and networks regularly to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. They can also conduct regular penetration testing to identify and address weaknesses in the organization’s security posture. | However, outsourcing testing requires planning before and is often done a few times only. The organization needs to define the scope of the testing and communicate it to the external security firm. This process can take some time and requires careful planning to ensure that the testing is comprehensive and effective. |
| Furthermore, an internal attacker has more comprehensive knowledge of an organization’s information system, as they have authorized access. This means that an authorized user can hack into an organization’s information system using either an internal or external system. Therefore, identifying vulnerabilities from an internal attacker’s viewpoint can help an organization better understand potential risks and take appropriate measures to prevent them. | Additionally, outsourcing testing is less comprehensive as it is done only to prevent an external threat. But you need to find a highly skilled security professional to perform an external security firm, as penetration testing companies often do not have the same level of access and knowledge of an organization’s information system as an internal security team. Therefore, they may not identify all potential vulnerabilities and may miss some critical risks. |
Conclusion
There are several tried and tested methodology to identify, exploit, and help address vulnerabilities for different kinds in internal and external penetration testing processes. It all depends on the use cases for example, Nokia uses penetration testing to ensure sound security of its web application. Based on your intuition, in-house security expertise, and target audience requirements, you can decide on whether you want external help to identify and mitigate security flaws within your application and infrastructure.