What Is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a process of opting for on-demand IT resources such as compute, storage, networking, databases, software, analytics, and intelligence, typically over the internet and on a pay-as-you-use basis. Rather than setting up their own computing infrastructure or data centers, businesses can rent computing resources from cloud service providers (or CSP). It saves the upfront cost of the companies and keeps them away from the complexity of owning and maintaining their own IT infrastructure. Whereas with cloud providers, businesses can pay as they use the resources.
Here’s a more official definition of cloud computing from the National Institute of Standards and Technology:
“Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.”
—The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing, National Institute of Standards and Technology
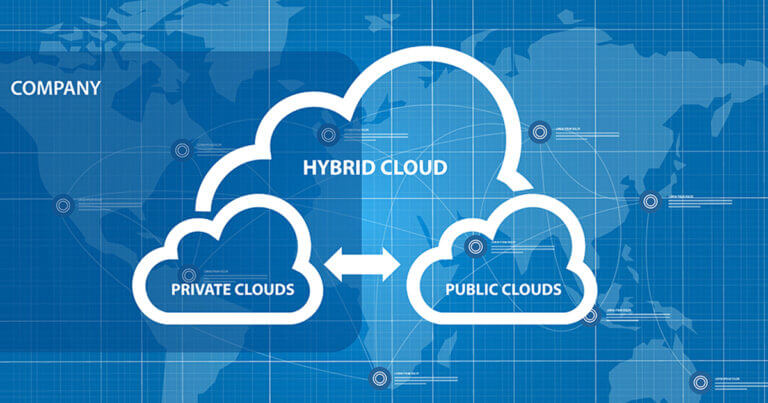
Types Of Cloud Computing Or Deployment Model
Not all clouds are the same, and not every cloud is a right fit for every business. Cloud computing offers many different services, models, and types to provide the right solution to companies based on their specific needs. However, we can classify cloud computing into three categories, such as:
Public Cloud
A third-party cloud service provider owns public clouds and offers computing services/resources, including storage, compute, over the internet. AWS and Microsoft Azure are good examples of public cloud. Third-party cloud providers own and manage all cloud resources such as hardware, software, and other infrastructure. Users get access to cloud resources through an account using a web browser.
Private Cloud
Private cloud, though it offers some of the advantages of public cloud, is considered best for businesses requiring optimum level security of data and services. Single companies widely consider private cloud resources to need ample computing power that scales on-demand without compromising security. A private network is used to maintain services and infrastructure in a private cloud.
Hybrid Cloud
A combination of a public and a private cloud is called a hybrid cloud. It allows data and applications to be distributed to multiple vendors and acquire different levels of cloud usage. Hybrid cloud offers a significant level of flexibility, deployment options and allows you to optimize existing infrastructure, security and compliance.
List Of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing has three primary service models like IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. Though there are apparent differences between cloud services and the advantages these offer to a business, they can also interact with each other and form one comprehensive cloud computing model. Let’s understand all three cloud computing services in brief below:
Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS)
Businesses can fulfill essential resources requirements, including computing, storage, and networking capabilities, using virtual servers known as Amazon EC2 in AWS and Microsoft Azure virtual machines in Microsoft Azure.
Platform As A Service (PaaS)
Businesses leverage PaaS to get computing power to build and run their applications. PaaS allows the deployment of custom applications to the cloud using AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Heroku. PaaS users simply choose from a menu to ‘spin up’ servers and environments they need in their project to run, develop, test, deploy, maintain, update, and scale applications.
Software As A Service (SaaS)
This cloud computing service combines infrastructure and software running in the cloud. SaaS applications run over the internet to various businesses who access it via the subscription model. Saas ensures cost savings, time-to-value, as well as manages automatic upgrades and protection from data loss. Amazon WorkSpaces, Google Apps for Work, and Microsoft Office 365 are a few examples of SaaS solutions.
What Can You Do With Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing offers numerous advantages to businesses. It supports organizations for faster innovation, provides flexible resources and economies of scale.
Implementing A Fault-Tolerant System Architecture
There are industries widely functioning with mission-critical applications. Mission-critical applications need to function continuously for a business to be successful. Even a brief downtime or failure of these kinds of apps can result in financial loss and lost productivity. Implementing a fault-tolerant system architecture with the help of cloud services ensures high availability and ensures business continuity.
Enabling Automation
Using cloud services, IT teams and admins can automate manual processes and speed up the delivery of infrastructure resources on a self-service basis. Cloud allows you to write code to create networks, build virtual server clusters, or deploy a relational database. Automation increases reliability and improves efficiency.
Scalability
Among several advantages of cloud computing, perhaps the biggest one is the ability to scale cloud environments on-demand. Cloud solutions provide businesses the ability to handle growing or diminishing resources to meet the business demands capably. Cloud computing offers a flexible capacity that frees the company from planning.
Built For Failure (Reliability)
As mentioned above, the cloud provides comprehensive support for fault tolerance or high availability. Meaning your business is always backed up with paralleled resources that sense service failure automatically and provide support instantly and prevent downtime to a great extent. Hence, the high availability of services naturally brings you reliability, even for free.
(With cloud computing and DevOps comes SRE (site reliability engineering) which is practiced to ensure high availability and reliability of systems or applications. Read here about SRE and how it helps ensure the reliability and availability of applications.)
Reducing Time To Market
Faster time to market means faster revenue that businesses cannot compromise. Cloud ensures reduced time to market because cloud servers take minutes to be booted and ready to use compared to physical servers that could take days or weeks to procure and provision. It brings super speed for businesses.
Worldwide Available
The speed of data flow is crucial – for instance, in e-commerce or stock trading. Deploying applications to data centers as close to target customers as possible makes a huge positive difference. Cloud service providers having multiple data centers at different locations allows worldwide availability with lower transaction costs.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is no longer in trend whereas it has become a business’s most crucial requirement that dreams of scaling and growing like no other. With varied deployment options, tools, technologies and payment methods make cloud and cloud-based computing a must for all sorts of businesses. Try it a free for a month and decide for yourself.